 Tamayakin’ initiative
Tamayakin’ initiative

Types and Classification of Surface Heat Treatment

 Return to list
Return to list
Overview.
Surface heat treatment includes surface quenching, in which only the surface is quenched and hardened, such as induction hardening, and thermal diffusion treatment, in which different elements such as carbon and nitrogen are infiltrated from the surface.
01 Thermal diffusion of atoms

The above figure schematically illustrates the diffusion of atoms in the contact zone when atom A is heated with atom B in contact with atom B. There are two types of solid solutions: one is an intrusion-type solid solution in which atom B forcefully enters the space of atom A , and the other is a substitution-type solid solution in which atoms are replaced by each other.
IN ORDER TO FORM AN INTRUSION-TYPE SOLID SOLUTION, THE SIZE OF ATOM B MUST BE SUFFICIENTLY SMALLER THAN THAT OF ATOM A. IN THIS CASE, ATOM B IS A NON-METALLIC ELEMENT SUCH AS CARBON (C) OR NITROGEN (N). IN MANY CASES, BOTH ATOMS ARE METALLIC ELEMENTS, AND THE SIZE OF THE ATOMS ARE COMPARABLE.
Depending on the combination of A and B, the concentration ratio may be the limit of possible solid solution ( solid solution limit ), compounds are formed. In many cases, such compounds are formed between metallic elements, and the formed compounds are called intermetallic compounds. When A is a metal atom and B is a nonmetal atom, it also belongs to an intermetallic compound.
02 Surface heat treatment applied to steel materials
Surface heat treatments for steel materials can be classified into surface quenching and thermal diffusion treatments, both of which involve the diffusion of atoms, as shown in the figure below.
| name | Surface Modification Phenomena | Main applicable steel grades | Main processing purpose | ||
| surface hardening | flame hardening | martensitization | Carbon Tool Steel for Machine Structural Steel in general | Abrasion resistance, fatigue resistance | |
| high-frequency quenching | |||||
| Laser hardening | Abrasion resistance of minute parts | ||||
| Electron Beam Quenching | |||||
| Thermal Diffusion Treatment | Diffusion Penetration Treatment of Nonmetallic Elements | carburizing and quenching | Carbon Diffusion | Low carbon steel in general | Abrasion resistance, fatigue resistance |
| nitriding | Nitrogen diffusion | All steel types | |||
| Carburizing and nitriding quenching | Carbon and nitrogen diffusion | Low carbon steel in general | Fatigue resistance, abrasion resistance | ||
| nitrocarburizing | Nitrogen and carbon diffusion | Machine structural steel Tool steel Stainless steel rope | |||
| oxynitridation | Nitrogen and oxygen diffusion | Seizure resistance, corrosion resistance | |||
| Sulfur dioxide nitriding |
Sulfur and nitrogen diffusion | Seizure resistance, abrasion resistance | |||
| Sulfurizing | Sulfur Diffusion | Structural steel in general | Seizure resistance, sliding properties | ||
| Boro nai jing (boronization) | Boron diffusion | Structural steel in general | Abrasion resistance, seizure resistance | ||
| Steam treatment (homo treatment) | Oxygen diffusion | Tool steel, structural steel | Seizure resistance, corrosion resistance | ||
| Diffusion penetration treatment of metallic elements | geladizing | Zinc Diffusion | Steel for machine structural use in general | Corrosion resistance (weather resistance) | |
| chromatizing | Chromium Diffusion | High temperature oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance | |||
| aluminizing | Aluminum Diffusion | ||||
| carbide crust | Formation of carbide layer | tool class | abrasion resistance | ||
Surface Heat Treatment of Steel Materials Surface Heat Treatment can be classified into surface quenching and thermal diffusion treatments, both of which involve the diffusion of atoms, as shown in the figure above.
surface hardeningisSurface hardening by heating and quenching only the necessary parts of the surfaceand the chemical composition does not change. In contrastThermal Diffusion TreatmentisBy heating the entire workpiece, foreign atoms other than iron (Fe) penetrate from the surface and diffuse toward the interior.The chemical composition of the surface after the treatment has changed.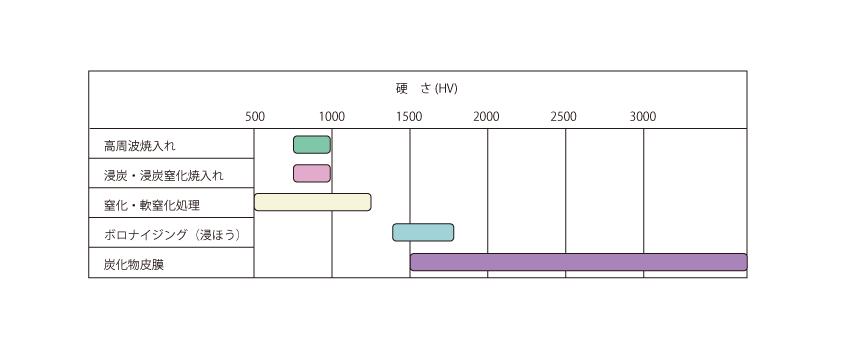
The main purposes of surface heat treatment are wear and corrosion resistance, and most of them belong to surface hardening treatment. As the above figure shows the hardness obtained by surface heat treatment, surface hardness obtained by surface quenching or carburizing is less than 1000 HV, while nitriding treatment can reach 1000 HV or more depending on the steel grade. In addition, carbide coating, in which carbide-forming elements such as vanadium and titanium are diffused, can achieve hardness of 3000 HV or higher depending on the type of carbide, contributing to improved durability of molds and other components.



