 Tamayakin’ initiative
Tamayakin’ initiative
Quenching (2) - Hardenability and Mass Effect

 Return to list
Return to list
Overview.
Hardenability is the performance that governs the hardening depth. Mass effect is the magnitude of the effect of the cross-sectional dimensions of the treated product on the hardening depth.
01 Hardenability
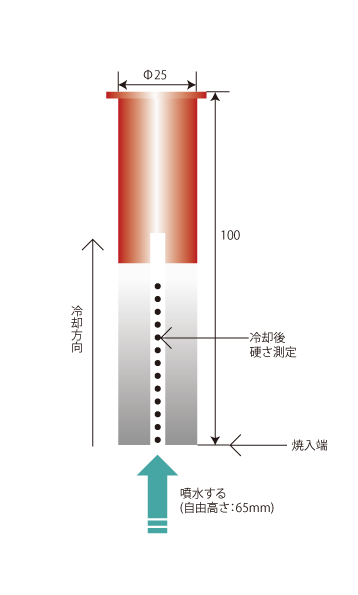
JIS G 0561 specifies a method for measuring the hardenability of steel called the "hardenability test method for steel (one-end hardening method). As shown in the figure below, this method measures hardenability using a cylindrical specimen of 25 mm in diameter and 100 mm in total length with a brim.
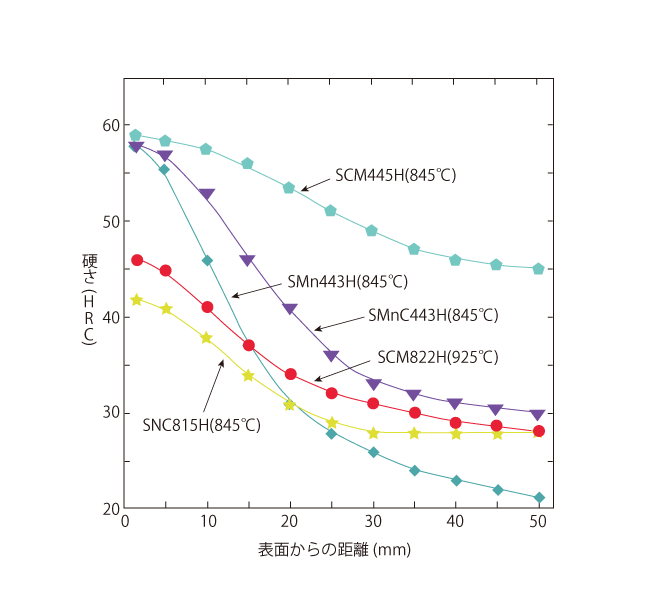
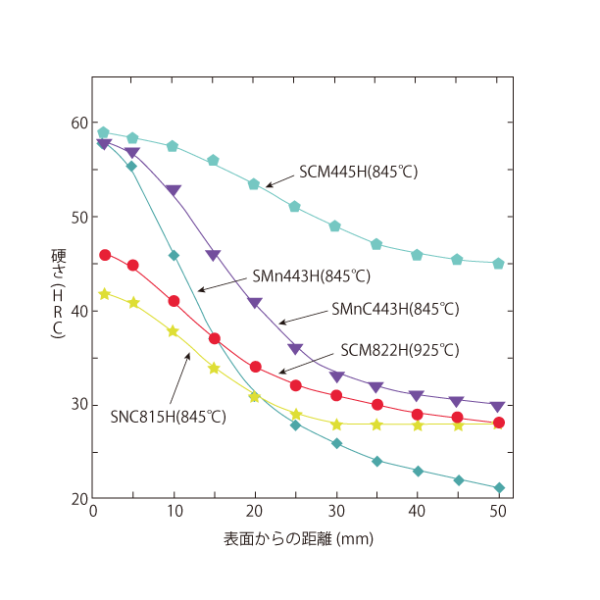
The above figure shows the hardenability curves for five structural taper steels with guaranteed hardenability, according to the intermediate values between the upper and lower limits. The hardness near the hardened end is higher for the tapes with higher carbon content, indicating that the maximum hardenability depends on the carbon content. In addition, the hardness transition curve from the hardened end clearly shows that alloying elements other than carbon (especially Cr and Mo) have an effective effect on hardenability.
02 Critical Diameter
Mass Effect refers to the degree to which the depth of the hardened hardening layer varies with the size of the cross-sectional dimension, and affects not only the properties of the steel but also the heating and cooling conditions during quenching.
The degree of quench hardening to the interior is generally Critical Diameter The critical diameter is the maximum diameter at which more than 50% martensite can be obtained to the center. The critical diameter is the maximum diameter at which more than 50% martensite can be obtained to the center. There are two factors that influence the critical diameter, one related to the material and the other to the hardening conditions, as shown in the figure below.
| element (e.g. in array, in programming, in programming) | effect | |
| material | Crystal grain size | The larger, the larger the critical diameter. |
| alloying element | Mn, Mo, Cr, and Ni increase critical diameter | |
| Quenching conditions | Quenching temperature | The higher the critical diameter, the larger the critical diameter. |
| Heating time | The longer the critical diameter, the larger the critical diameter. | |
| coolant | The larger the cooling capacity, the larger the critical diameter. | |
03 Effect of alloying elements, quenching temperature, and quench coolant on mass effect
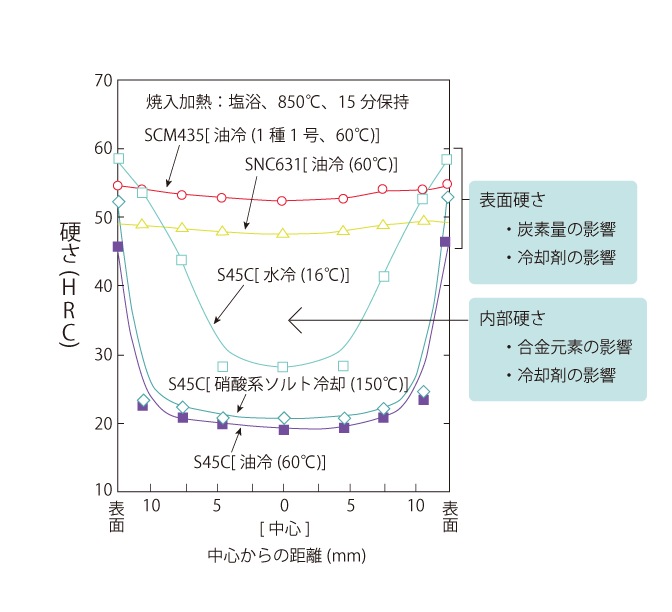
The above figure shows the hardness distribution in the center cross section of various machine structural steels of 25 mm in diameter and 55 mm in length when quenched from 850°C. Clear differences between the steels are observed, clearly indicating the important role of alloying elements on the mass effect.

In addition, three different quenching temperatures and three different quenching coolants were used for SK85, which is a eutectoid carbonaceous rope. quenching coolant The following table shows the effects of three different quenching temperatures and three different quenching coolants on SK85. The surface hardness values are identical regardless of quenching temperature and quenching coolant, but quenching from a higher temperature is advantageous in terms of mass effect. Among the coolants, water has the greatest cooling capacity, while oil and salt are found to be comparable.



