 Tamayakin’ initiative
Tamayakin’ initiative

 Return to list
Return to list
01 Galvanizing to protect steel at the expense of self
Zinc (Zn) plating is widely used for the purpose of corrosion protection of steel, and is an economically advantageous surface treatment with a longer corrosion protection period than other surface treatments. The principle of this corrosion protection is that Zn, which is more easily corroded than iron (Fe), becomes an anode and dissolves in a moist environment, thus protecting the underlying steel from corrosion. Zn dissolves, the steel is protected from corrosion for a long period of time.
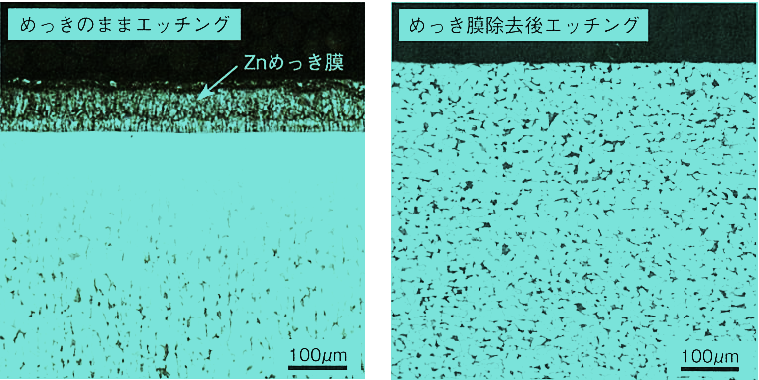
The figure shows the cross-sectional microstructure of Zn-plated S15C. When etching is performed to reveal the microstructure without removing the plating, the area directly below the plating film is almost completely unetched. The etched material with the Zn film removed is uniformly etched over the entire surface, indicating how significant the presence of Zn is.



