 Tamayakin’ initiative
Tamayakin’ initiative
Tempering (1) - Hardness and mechanical properties

 Return to list
Return to list
Overview.
Although the purpose of tempering varies with the grade and treatment, a significant improvement in toughness over the as-quenched version is a common effect for all grades.
01 Purpose and Method of Tempering
Quench-hardened steel materials are very brittle as they are, so even cutting tools and knives, for which wear resistance is of paramount importance, must be tempered before use. Tempering Tempering is also used for machine structural steels. Tempering is also used to adjust the mechanical properties of machine structural steels in the final product.
Tempering temperatures in the low temperature range of 100~200°C or in the high temperature range of 400~650°C are used depending on the purpose. low temperature tempering and the latter is called high temperature tempering The former is called low-temperature tempering and the latter is called high-temperature tempering. The common mission of tempering is to sufficiently precipitate supersaturated solid-solution carbon as carbides, so sufficient heat retention is necessary.
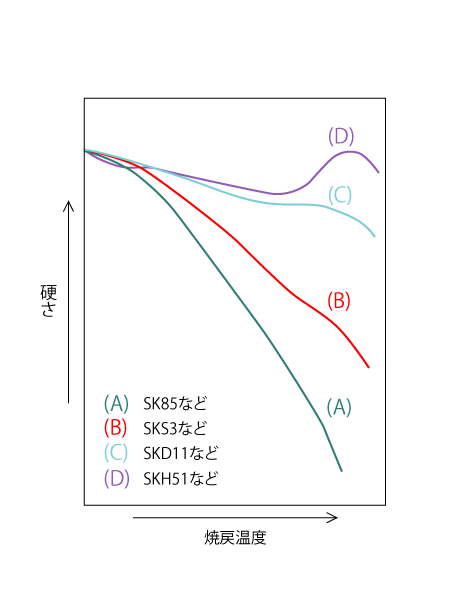
02 Hardness change due to tempering
In general, tempering reduces hardness, but the degree of hardness depends on the grade.

THE ABOVE FIGURE SHOWS THE HARDNESS TRANSITION AS A FUNCTION OF TEMPERING TEMPERATURE, ASSUMING VARIOUS TYPES OF TOOL STEELS. AS SHOWN IN (A), THE HARDNESS OF CARBON STEEL DECREASES RAPIDLY AT HIGHER TEMPERING TEMPERATURES, BUT THE ADDITION OF ALLOYING ELEMENTS INCREASES THE RESISTANCE TO TEMPER SOFTENING. IN PARTICULAR, IN THE CASE OF HIGH-SPEED TOOL STEEL, THE HARDNESS IS HIGHER THAN THE QUENCHED HARDNESS DUE TO TEMPERING, AS SHOWN IN (D).
03 Relationship between hardness and mechanical properties
Since hardness is an important factor in determining mechanical properties, hardness is specified when requesting heat treatment and is controlled by hardness during heat treatment.
Shape and dimensions of mechanical test specimens
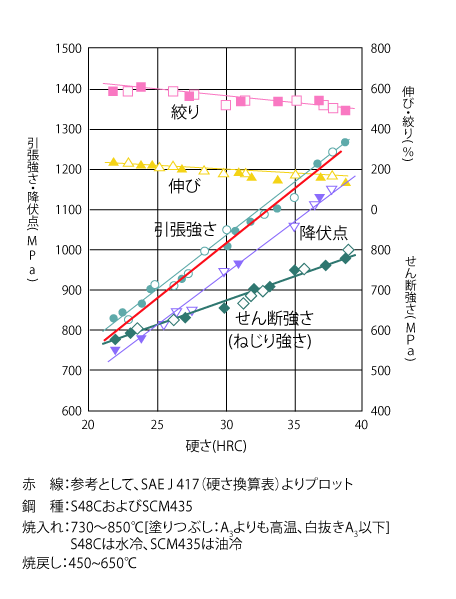
Relationship between Tempered Hardness and Mechanical Properties of Machine Structural Steels
Relationship between Tempered Hardness and Impact Value of Machine Structural Steels
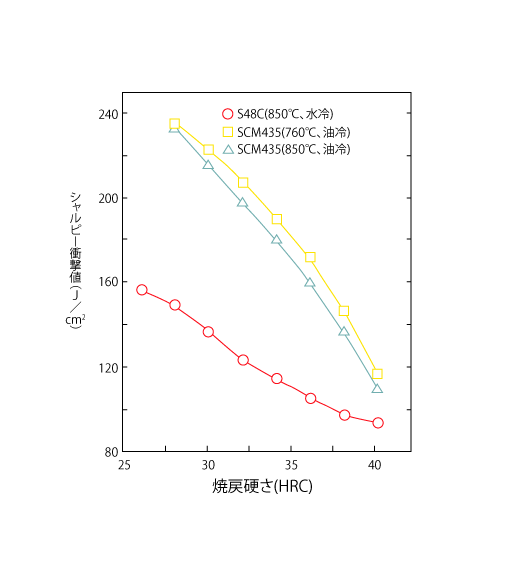
USING THE ABOVE MECHANICAL SPECIMENS, TENSILE AND IMPACT TESTS WERE CONDUCTED ON MACHINE STRUCTURAL STEELS (S48C AND SCM435) TO SHOW THE RELATIONSHIP WITH HARDNESS, RESPECTIVELY.
It is clear from these figures that hardness dominates for all values. The red line in the tensile strength section is plotted from the hardness conversion table for reference, which is also in good agreement with this test result. However, even though the hardness is the same, the impact values are greatly influenced by alloying elements as well as heat treatment conditions, clearly showing the superiority of alloy ropes for machine structural use over carbon steel.



