 Tamayakin’ initiative
Tamayakin’ initiative

 Return to list
Return to list
Overview.
When steel materials are used in products or components that are subject to rising temperatures, material properties such as thermal expansion coefficient and high-temperature hardness must be considered.
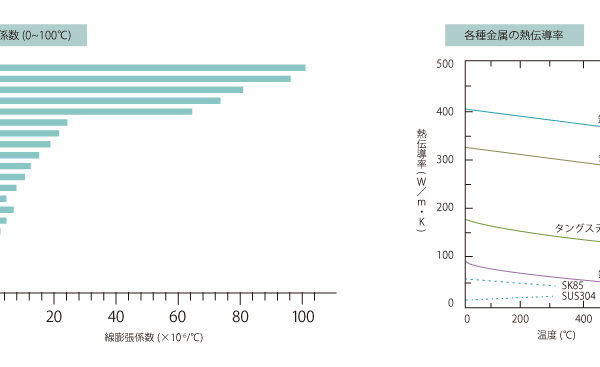
01 Coefficient of thermal expansion and thermal conductivity
As shown in the above graph, among the various materials, the coefficient of linear expansion of metals is in the middle, smaller than that of resins and larger than that of ceramics.
Among metals, the coefficient of linear expansion of iron is larger than that of titanium, but smaller than that of copper and aluminum.
Also, the thermal conductivity of iron is much smaller than that of copper or gold.
Moreover, the thermal conductivity of high-carbon steel containing carbon is even lower, and stainless steel is less than 1/3 that of iron.
However, at temperatures above 800°C, the difference disappears and the thermal conductivities become comparable.
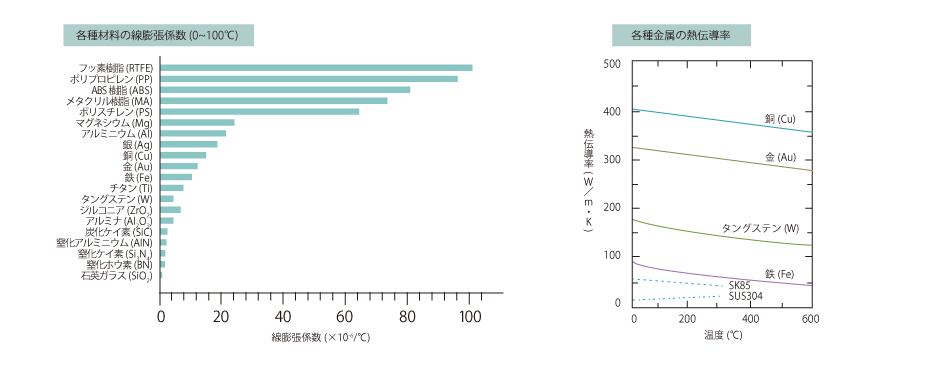
02 Volume resistivity and high temperature hardness
The volume resistivity of the various working elements shows exactly the opposite of the thermal conductivity graph.
The volume resistivity of iron is much higher than that of gold or copper, indicating that it does not conduct electricity well.
Regarding the high-temperature hardness of machine structural steel and stainless steel, machine structural steel softens rapidly at temperatures above 500°C, whereas stainless steel maintains its hardness gently as the heating temperature rises.
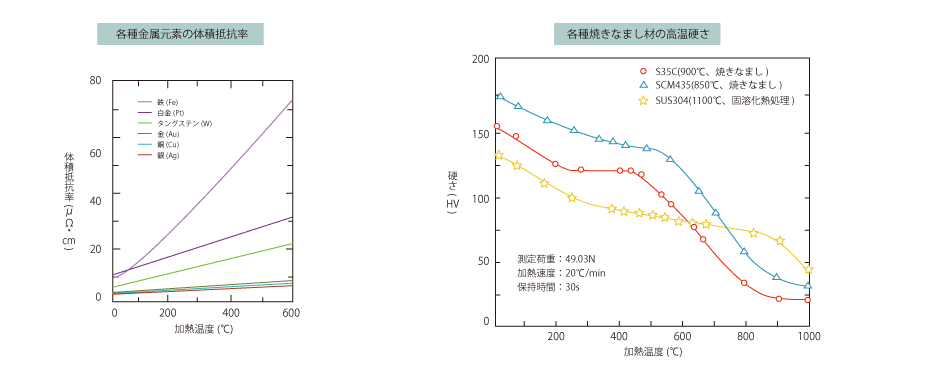
It has also been shown that the hardness of carbon steel after quenching is similar at temperatures above 500°C, even though there is a difference at room temperature.
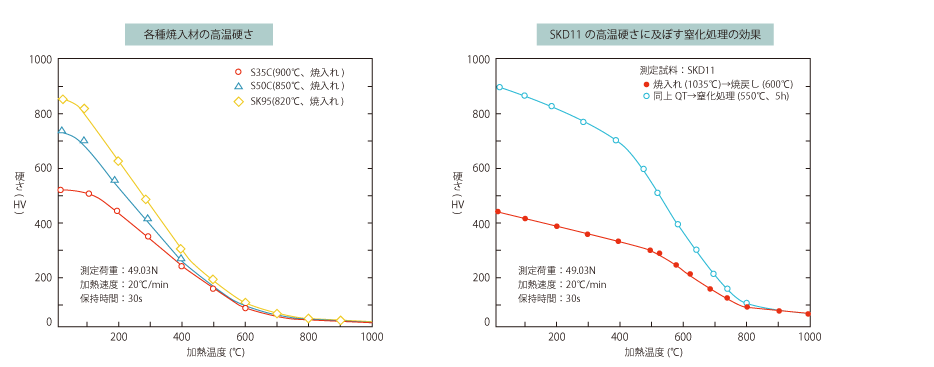
AND NOW FOR THE QUENCHED AND TEMPERED SDK11. NITRIDING TREATMENT SIGNIFICANTLY INCREASES HARDNESS AT ROOM TEMPERATURE, INDICATING THAT NITRIDING TREATMENT IS EFFECTIVE UP TO ABOUT 800°C.



