 Tamayakin’ initiative
Tamayakin’ initiative
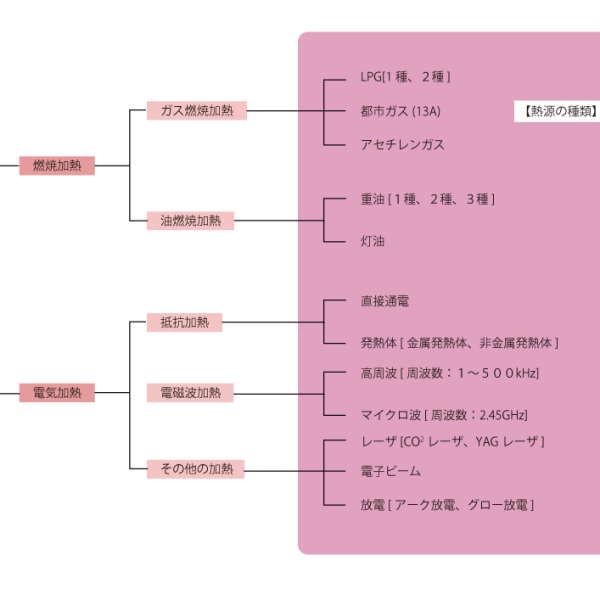
Heating Furnace ① - Classification by Heat Source

 Return to list
Return to list
Overview.
In heating furnaces, there are two types of heating methods: combustion heating and electric heating.
01 Types and Features of Combustion Furnaces
Heating equipment can be classified by heat source into combustion furnaces with combustion heating and electric furnaces with electric heating, each of which has a direct heating method and an articulated heating method.
Combustion furnaces use liquid or gas as fuel, the former being heavy oil or kerosene and the latter being city gas or liquefied natural gas. Heavy oil and city gas are often used in large heating furnaces that use large amounts of fuel, because their fuel costs are lower than those of electricity. There are two types of heating methods: direct heating, which uses a combustion burner for direct heating, andindirect heating, which uses radiant tubes or retorts for heating.
The direct heating method is difficult to precisely control the furnace temperature and obtain uniform temperature distribution, and the heating atmosphere cannot be controlled due to the effect of combustion gases, so the types of heat treatment available are limited. In other words, this method is often used for annealing of temporary products (materials, cast iron, cast steel, etc.) where precise temperature control and surface deformation caused by heating are not a major concern.
The indirect heating method is also used in furnaces for bright heat treatment and carburizing and quenching because it is easy to precisely control the furnace temperature and has absolutely no effect on the heating atmosphere.
The indirect heating method is also used in furnaces for bright heat treatment and carburizing and quenching because it is easy to precisely control the furnace temperature and has absolutely no effect on the heating atmosphere.
02 Types and Features of Electric Furnaces
Electric furnaces are often used for items for which temperature control is important because of their ease of temperature control. As in the case of combustion furnaces, there are two types of heating methods: direct heating and indirect heating, with the latter generally used. The direct heating method directly energizes the workpiece, which facilitates rapid heating, but since the temperature rise is due to the electrical resistance of the workpiece, the shape of the workpiece has a large influence, so the workpiece is limited to wire rods of simple shapes.
Indirect heating methods include heating elements, high-frequency coils, lasers, and electron beams. The most common type uses a heating element, as shown in the figure below. Heating element As shown in the figure below, there are two types of heating elements: metal heating elements such as nichrome and non-metal heating elements such as silicon carbide and carbon. Depending on their characteristics, they are used in all types of heat treatment, including quenching, tempering, carburizing, nitriding, and bright heat treatment.
| name | Max. operating temperature | Features, Applications | ||
| Metal heating elements | Nichrome | Ni-Cr alloy | 1200 | The most common heating element, widely used in various heat treatment furnaces and electric heating equipment up to 1000°C |
| cantaloupe | Fe-Cr-Al alloy | 1400 | Can be used up to higher temperatures than nichrome, so it is applied to high-temperature industrial furnaces up to about 1200°C. | |
| molybdenum disilicide | MoSi2 | 1800 | Mainly used in the atmosphere and applied to high-temperature sintering furnaces and sintering furnaces for ceramics | |
| Non-metallic heating elements | molybdenum (Mo) | Mo | 1500 | Cannot be used in air, but applied to various atmosphere furnaces and vacuum heating furnaces |
| silicon carbide (SiC) | SiC | 1600 | Generally, it is a rod or tubular heating element and is applied to heating furnaces up to about 1400°C. Large change in electrical resistance with temperature. | |
| carbon | C | 3000 | Although it cannot be used in air, it can be easily manufactured in various shapes, such as bars and flat plates, and is applied to atmosphere heating furnaces and vacuum heat treatment furnaces. | |
| alumina | Al2O3 | 1000 | Heating elements in the form of flat plates or rods, which are small, high-power and fast heating rate, and are applied to warm-air heaters for heating and drying, and ignition heaters. | |



